Report on Polygenic Traits
Polygenic traits are traits, such as height or weight, that are caused by the action of multiple genes. In addition to genetics, polygenic traits are influenced by many other factors, such as environment, socioeconomic factors, and lifestyle. The genetic component of polygenic traits is assessed using polygenic risk score (PRS). PRS incorporates the effects of many genetic variants into one number that predicts the genetic predisposition for trait. Each PRS value can be plotted on a PRS distribution frequency plot (the bell-shaped curve). For most people, their PRS values will be in the middle region, but for some, these values may deviate to the left or right of the average, which will indicate the presence of a lower or higher value of the polygenic trait.
To calculate polygenic traits, predictive models (logistic regression model and Cox regression model) are used that take into account PRS values, as well as parameters such as sex and age (allowable range: from 18 to 80 years). Polygenic risk models are a vector of variant effect scores identified for a trait based on the results of genome-wide association studies and taking into account the structure of linkage disequilibrium. The models are constrained by a list of common genetic variants represented in the HapMap 3 data set. The logistic regression model allows you to determine the relationship between the presence or absence of a disease and predictor variables. The Cox regression model takes into account the age of onset of the disease and, accordingly, allows you to see the dynamics of the risk of developing the disease with age. More about comparing these models: Ingram DD, Kleinman JC. Empirical comparisons of proportional hazards and logistic regression models. Stat Med. 1989 May;8(5):525-38. The final prediction of the models is not absolutely accurate, since the list of genetic variants influencing polygenic traits is constantly being supplemented by the scientific community. How well a statistical model predicts the presence or absence of a disease in a person is determined by the AUC (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve) index. The AUC value ranges from 50% to 100%, where higher values indicate that the model has more predictive power.
Report generation#
The report is based on the "Polygenic traits" report template block, which can only be applied to non-tumor samples. The block regulates polygenic risk score calculation results for which traits will be included in the report.
Report on polygenic traits is generated for a sample if the following conditions are met:
- The sample is uploaded as a non-tumor sample (a sample of the "NORMAL" type).
- The sample analysis has been successfully completed (i.e. all stages included in the workflow have the "Complete" status).
- The "Polygenic risk scores calculation" task of the "Genomic predictions" analysis stage has been successfully completed for the sample. By default, the task is not included in the analysis workflow, so it must be included in the parameters by activating the "Run polygenic risk scores calculation" option. Please note that to include polygenic risk scores calculation in the analysis workflow of a sample uploaded in VCF or GT format, you must select the setting preset, which includes the "Run polygenic risk scores calculation" parameter, at the stage of composing a sample set.
- The report template, which includes the "Polygenic traits" block, is active (adjusted on the "Report templates" page).
- The report template was added to the system before the sample processing has been completed.
After a report on polygenic traits has been successfully generated, open the report tab from the sample page. To calculate a report, you must specify the patient's age (date of birth) and sex, which are taken into account when building a predictive model for calculating polygenic risk scores. This can be done on the patient page or on the report page itself. If the patient is under 18 years old, the extreme lower limit will be used as the age value of 18 y.o. for calculations, since the predictive model uses a range from 18 to 80 years old. If the patient is over 80 years old, the extreme upper limit will be used as the age value of 80 y.o. for calculations, since the predictive model uses a range from 18 to 80 years old. If the patient's sex is not specified, the sex value determined from genetic data is used (the "Determining sex" task of the "Genomic predictions" stage). After specifying the patient's age and sex, you need to wait a bit while the values required for generating the report are calculated.
Results#
Which polygenic traits will be included in the report is defined in the report template block. Quantitative and binary polygenic traits are available for selection.
Prediction results for quantitative polygenic traits#
A quantitative trait defined by a numerical value, often determined by multiple genes at different genomic locations that have small effects and are influenced by environmental conditions. For such traits, the predicted value is estimated from a predictive model using the PRS value and the patient's sex and age. This dimension of this value is of the given trait, so it can be easily interpreted. Since the predictive model determines a trait value with a certain error, a confidence interval is provided for each trait, giving the information about the range of possible values. The confidence interval is calculated from the parameters of the predictive model.
Quantitative polygenic risks calculated:
- Height
- Weight
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
As prediction results for quantitative polygenic traits, the following information is provided:
- Predicted trait value is the absolute trait value determined using a logistic regression model that takes into account the patient’s genetic data and data on sex and age. In the diagram below, the predicted trait value is the patient's genetic height (162 cm).
- The range of possible trait values is the 95% confidence interval, which includes the true value of the trait with a high degree of confidence (the logistic regression model is used for calculation). In the diagram below, the range of possible values is a height from 153 cm to 172 cm.
- A comparison of the predicted value with the mean value of the trait. The result of the comparison is a conclusion about how much the patient's predicted value of a given trait is less or more than the average value of the trait, determined taking into account the patient's ethnicity, as well as his sex and age. In the diagram below, the average value of the trait is the average genetic height (166 cm).

- A display of a patient's polygenic risk score (PRS) value on a PRS distribution graph. The patient’s PRS value area is marked green (if values fall in the low or average PRS range) or orange (if values fall in the high PRS range) and the remaining area is blue. In the graph below, the patient's PRS values deviate to the left of the average PRS range, indicating lower values of the polygenic trait:
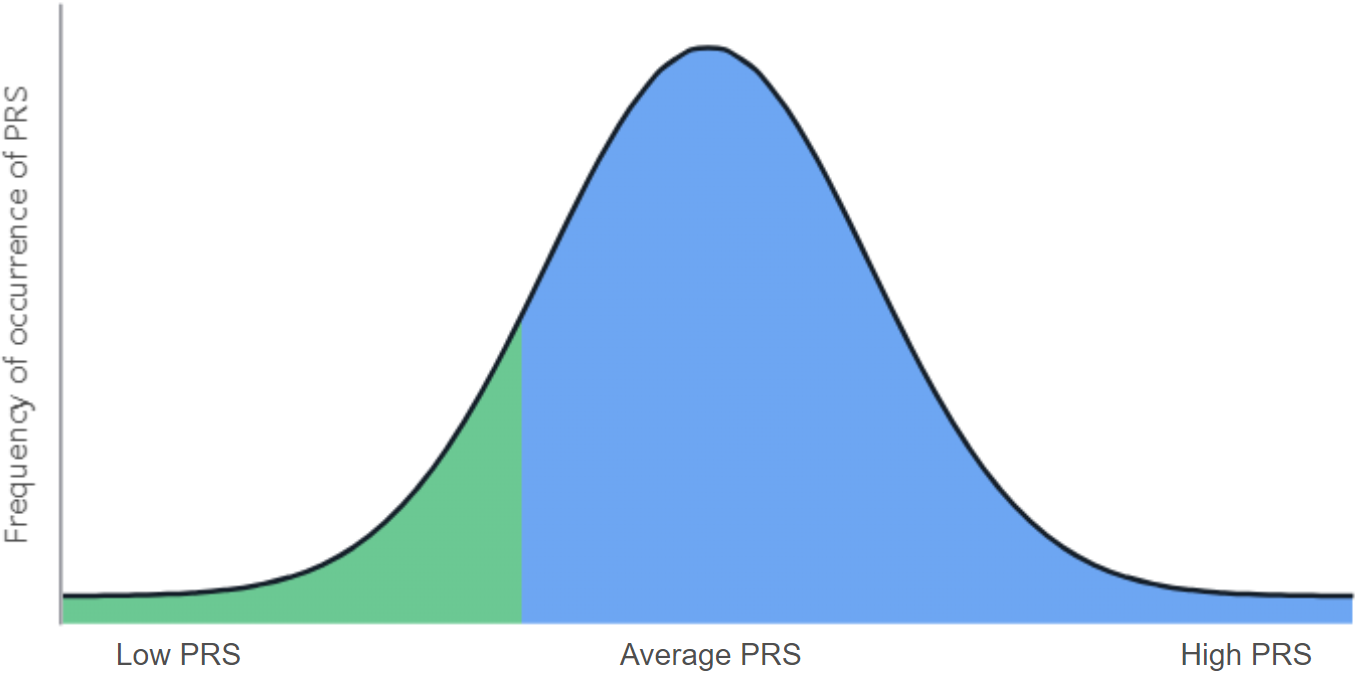
We also determine how much the absolute value of the patient's trait differs from the average value of the trait of people from a group of close ethnic origin. As the result of comparison, the percentage of the number of people, who have a genetic prognosis of the trait lower or greater than the patient, is given.
Prediction results for binary polygenic traits#
Binary traits are characteristics with two possible outcomes: presence or absence (e.g. susceptibility or resistance to a certain infection).
Binary polygenic risks calculated:
- Predisposition to being overweight
- Predisposition to Prostate Cancer (if the patient's sex is indicated as male)
- Predisposition to Breast Cancer (if the patient's sex is indicated as female)
- Predisposition to Coronary Artery Disease
- Predisposition to Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Predisposition to Type 2 diabetes
- Predisposition to Colorectal Cancer
As prediction results for binary polygenic traits, the following information is provided:
- Predicted value of the patient's predisposition to the trait determined using a logistic regression model that takes into account the user’s genetic data and data on age and sex. It's presented in the diagram as a "Patient risk" block. The block is colored green if the patient’s risk is less than the mean risk, or orange if the patient’s risk is greater than the mean risk. In the diagram below, the predicted trait value (the risk of developing the disease) is 21%.
- A comparison of the predicted value with the mean risk. Comparison is presented as a diagram. The mean risk of disease is determined by the patient's ethnicity as well as sex and age, and is presented in a blue-coloured "Mean risk" block. In the diagram below, the mean risk value of the trait is 12%. As a result, information is provided on how many times the patient’s genetic risk for the trait is greater or less than the average risk of people from a group of close ethnic origin.

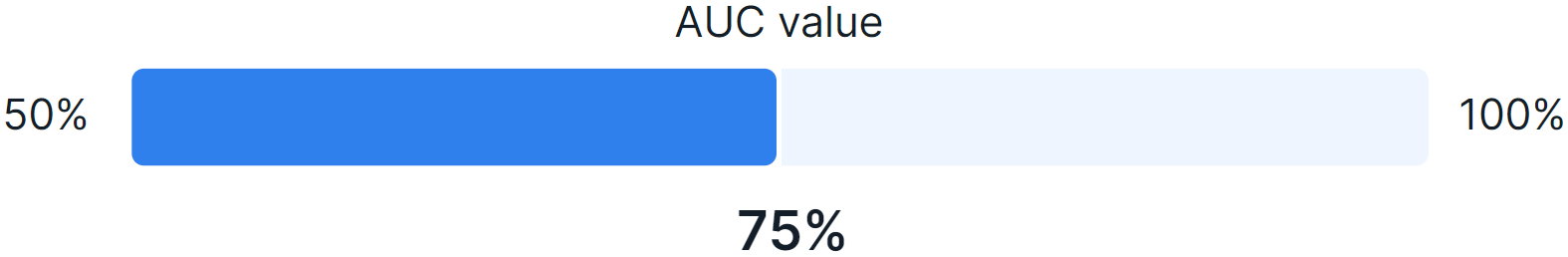
- The quality of model prediction (in percent) observed using the AUC (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve) score for calculation of genetic predisposition to a certain disease. In the diagram below, the model prediction quality is 75% for the trait under study and patient's ethnic group.
- A display of a patient's polygenic risk score (PRS) value on a PRS distribution graph. The patient’s PRS value area is marked green (if values fall in the low or average PRS range) or orange (if values fall in the high PRS range) and the remaining area is blue. In the graph below, the patient's PRS values deviate to the right of the average PRS range, indicating greater values of the polygenic risk:
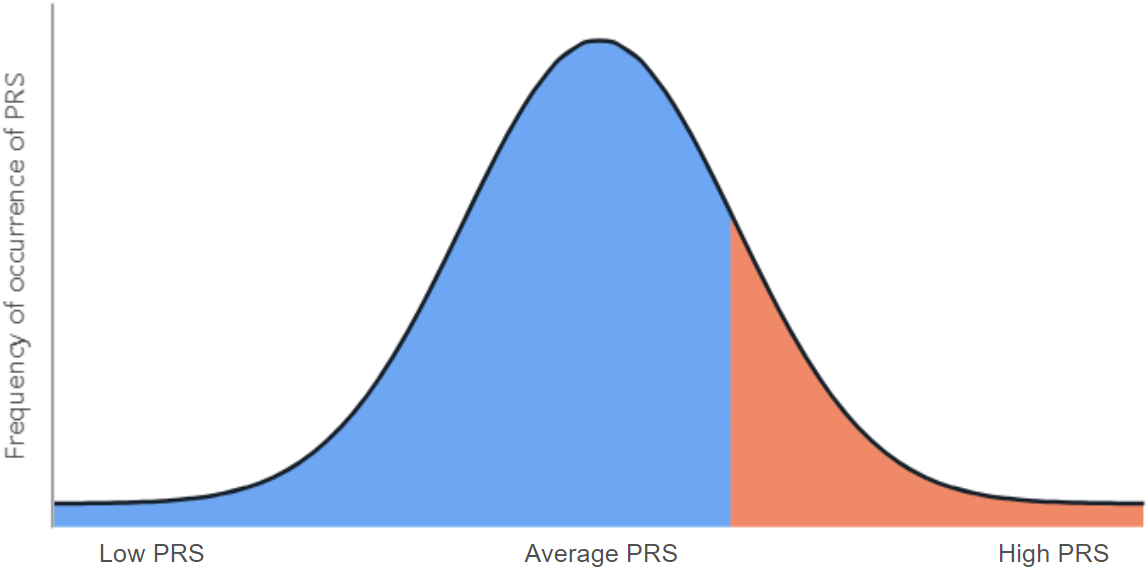
It is also determined how much the patient's polygenic risk score value differs from the distribution of the values of the polygenic risk scores of people from a group of close ethnic origin. As the result of comparison, the percentage of the number of people, who have a genetic risk of the trait lower or greater than the patient, is given.
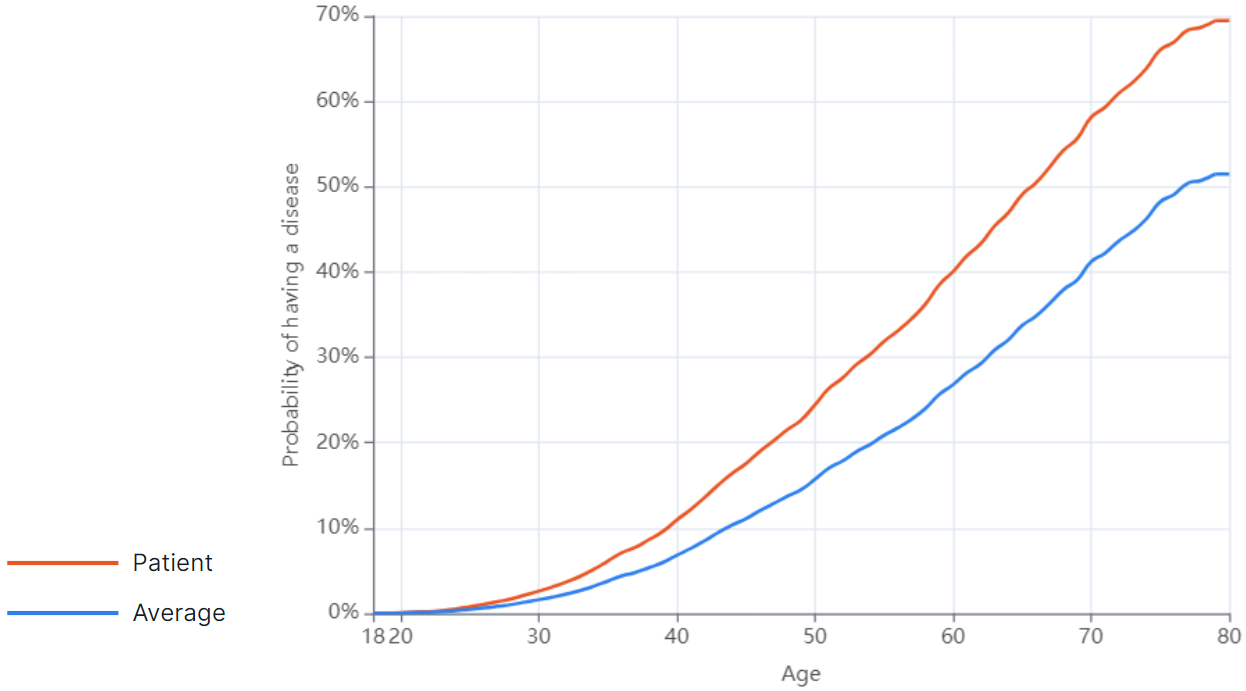
- A graph of disease risk versus age, taking into account the patient's genetic predisposition and comparing this risk value with the average results of people of similar ethnic origin. The probability of having a disease based on age is presented as a graph. The patient’s disease risk curve is marked green (if the patient’s disease risk is below average) or orange (if the patient’s disease risk is above average), and the average disease risk curve is marked blue.
An example of a graph showing a patient's risk of having a disease based on age is below average:
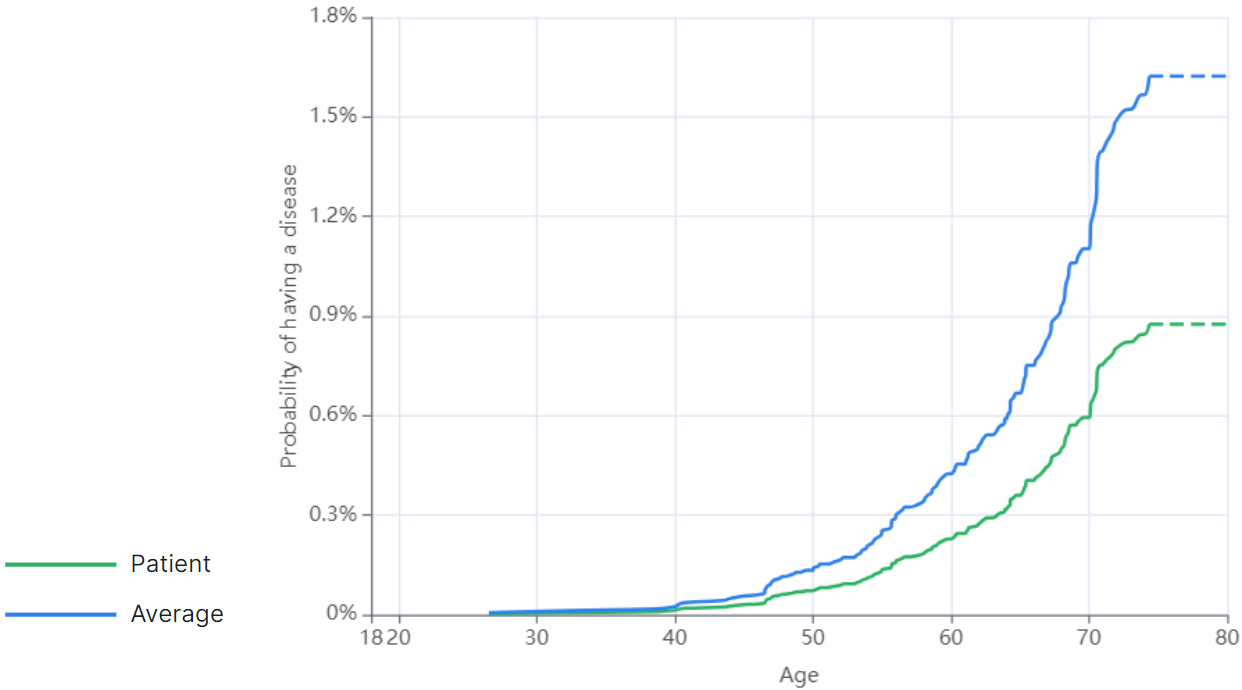
An example of a graph showing a patient's risk of having a disease based on age is above average: