Mutations Suitable For The Specified Conditions
The report includes SNVs/Indels or copy number variations (CNVs) discovered in the sample and suitable for the certain conditions that the user can set in the report template. Once you have selected the conditions you are interested in, you can customize the report to include mutations that are most relevant to your study. For example, you can fill the report with clinically significant mutations; mutations associated with a specific phenotype; mutations localized in certain genes, etc.
SNVs/Indels suitable for the specified conditions#
The report includes SNVs/Indels discovered in the sample and suitable for the conditions specified in the "SNVs/Indels suitable for the specified conditions" report template. Drawing up conditions for variants is described here.
SNVs/Indels included in the report are presented in the form of a table with the following columns:

- Potential finding icon
. Displayed if the option "Use SNVs/Indels suitable for the conditions specified in the block as potential findings" was enabled in the report template. Working with potential findings is described in the corresponding section.
- Gene is the common name of the gene in which the variant is located. If you click on a gene, you will see a window with all the gene transcripts:

You can find the description of the transcripts' table columns in the description of "Transcripts" section on the variant details panel.
- Position is a coordinate of the variant in the genome (chromosome + start position).
- Genetic variant is the nucleotide and amino acid substitutions using the HGVS notation. Nucleotide substitution: “c.” (coding; for a substitution in the coding sequence) or “n.” (non-coding; for a substitution in the non-coding sequence) prefix + genomic position of the substituted nucleotide + reference allele > alternative allele. Amino acid substitution: “p.” prefix (protein) + reference amino acid + amino acid position in protein + new amino acid resulting from the substitution.
- Transcript is the main transcript ID from the RefSeq database (NM_xxxxxx.x). If you click on a transcript, you will see the same window with all the gene transcripts, as when you click on the "Gene" field.
- Consequence is the effect of the variant on genes. A detailed description of the possible values can be found here.
- Allele frequency is an alternative allele frequency for the sample (in percentages).
- Coverage depth is a sequencing depth; the total number of reads of the sequence overlapping the variant position for the sample.
- External links are links to pages with variant information in dbSNP, ClinVar and COSMIC (if it was uploaded as a custom annotation).
- Links to the variant in embedded services:
is a module for visualization of variant on the genome,
is a variant details page in SNV Viewer ("Annotation" tab).
The variant interpretation text may be given below the variant row if it was added as described here.
CNVs suitable for the specified conditions#
The report includes copy number variations (CNVs) discovered in the sample and suitable for the conditions specified in the "CNVs suitable for the specified conditions" report template. The filtering parameters available for drawing up conditions for variations are described here.
You also have to select CNV region type in the report template: segments (large regions of the genome that are obtained by combining adjacent bins with similar copy number) or bins (small intervals which are created by dividing the reference genome into equal-sized intervals).
Example of a segment in a report:
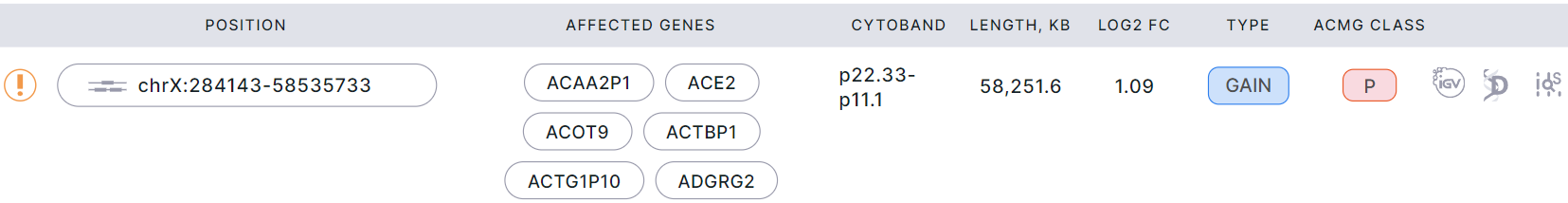
Example of bins in a report:
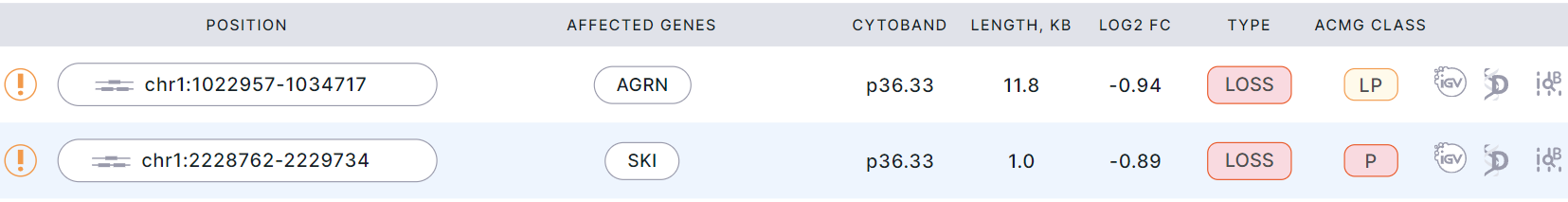
The table with variations in the report has the following columns:
- Potential finding icon
. Displayed if the option "Use CNVs suitable for the conditions specified in the block as potential findings" was enabled in the report template. Working with potential findings is described in the corresponding section.
- Position is a coordinate of the variation in the genome (chromosome + start position + end position).
You can copy the variation position to the clipboard by moving the cursor over the column value and
clicking on
.
- Affected genes are names of genes located in the area affected by the variation. Clicking on a gene badge opens its page in OMIM (if available) or Ensembl.
- Cytoband is a shorthand notation for the CNV position on a chromosome. This position is indicated relative to bands (regions of chromosomes that are clearly different from neighboring ones) that are formed on chromosomes by differential staining methods. A region is a section of a chromosome arm between the two closest marker bands (the most noticeable and clear light or dark bands). Sub-bands are sections of chromosomes resulting from the division of bands when analyzing chromosomes with high resolution. Sub-bands can also be divided into parts. The nomenclature of the CNV locus is as follows: chromosome arm (p-arm, i.e. shorter arm, or q-arm, i.e. longer arm), region, band, sub-band (can also be divided into parts). For example, the “p.36.33” locus means that the variation is located in the 3rd part of the 3rd sub-band of the 6th band of the 3rd region of the p-arm of the chromosome.
- Length, kb is a length of the copy number variation region in kilobases.
- Log2 FC is the logarithmic ratio of the detected copy number to the normal copy number (equals to 2 for autosomes and the X chromosome in the case of genotype XX, or to 1 for sex chromosomes in the case of genotype XY).
- Type is a copy number variation
type:
- deletion,
- duplication.
- ACMG Class is the variation pathogenicity assigned according to the ranking score defined
by AnnotSV. Column values are presented
as icons:
- Pathogenic;
- Likely pathogenic;
- Uncertain significance;
- Likely benign;
- Benign.
You can see the full value by hovering over the icon. - Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV), i.e. a module for visualization of variation on the
genome:
.
To see simultaneously two border regions of the quite large variation in IGV, click on, and to return to the visualization of the entire variation, click on
. If you would like to go to the position opened in IGV in Decipher genome browser, click on
. If you want to open CNV Viewer with a filter by the position opened in IGV, click on
.
- Link to variation position
in Decipher genome browser:
.
- The CNV position (displayed in a tree mode
with split records)
in CNV Viewer, i.e. embedded service
for viewing and analyzing copy number variations. The button to open CNV Viewer looks like
this for segments:
, and like this for bins:
.
Report export#
A report with variants or variations that meet the specified conditions can be downloaded in PDF format.
To do this, click on the button in the
upper right corner of the report page.