Onco-Genetic Testing Report
The report contains onco-relevant variants discovered in the sample and included to the report by the user, and clinical guidelines corresponding to these variants.
caution
The results of the report should be interpreted using all available clinical and laboratory data and should not be used in isolation for diagnosis and treatment.
To get a report, do the following:
- Create a report template that includes "Onco: Onco relevant SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" and "Onco: Clinical Guidelines for onco relevant SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" blocks.
- Include the required onco-relevant variants to the report. You can do this on SNV Viewer page or on the variant details page.
Report Section with Onco-Relevant Variants#
- Corresponds to "Onco: Onco relevant SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" template block.
- If no onco-relevant variants were included to the report, then the report will contain the message “You can mark onco-relevant variants in SNV Viewer to add them to this section”. If the sample interpretation has been completed, then the report will contain the message "Interpretation completed, no onco-relevant variants added to the report". However, onco-relevant variants can be included to the report after the interpretation has been completed.
- Onco-relevant variants added to the report are presented in a table with the following columns:

- Gene is the common name of the gene in which the variant is located. If you click on a gene, you will see a window with all the gene transcripts:

You can find the description of the transcripts' table columns in the description of "Transcripts" section on the variant details panel.
- Position is a coordinate of the variant in the genome (chromosome + start position).
- Genetic variant is the nucleotide and amino acid substitutions using the HGVS notation. Nucleotide substitution: “c.” (coding; for a substitution in the coding sequence) or “n.” (non-coding; for a substitution in the non-coding sequence) prefix + genomic position of the substituted nucleotide + reference allele > alternative allele. Amino acid substitution: “p.” prefix (protein) + reference amino acid + amino acid position in protein + new amino acid resulting from the substitution.
- Transcript is the main transcript ID from RefSeq database (NM_xxxxxx.x). If you click on a transcript, you will see the same window with all the gene transcripts, as when you click on the "Gene" field.
- Consequence is the effect of the variant on genes. A detailed description of the possible values can be found here.
- Allele frequency is an alternative allele frequency for the sample (in percentages).
- Coverage depth is a sequencing depth; the total number of reads of the sequence overlapping the variant position for the sample.
- Mutation class according to the classification of mutations by clinical significance:
| Mutation class | Mutation level | Description | Mutation type |
| I | A | Variants with high clinical significance included in clinical guidelines (RUSSCO, АОР, etc.) for the treatment of a certain type of tumor | LoF-variants: missense, nonsense, insertions/deletions, canonical ±1 or ±2 splice sites, chromosomal rearrangements |
| B | Variants with high clinical significance identified in large-scale studies and with consent of Russian experts in this field for certain types of malignant neoplasms | ||
| C | Variants with high clinical significance, identified in large-scale studies and with consent of foreign experts in the field for the treatment of certain types of malignant neoplasms | ||
| II | D | Variants with potential clinical significance recommended for other indications or for the treatment of other tumor types | LoF-variants: missense, nonsense, insertions/deletions, canonical ±1 or ±2 splice sites, chromosomal rearrangements |
| E | Variants with potential clinical significance identified in preclinical studies for the treatment of this oncological disease | ||
| III | Somatic variants of uncertain clinical significance: located in genes not associated with the development of cancer, or have no evidence to establish their pathogenicity and have low minor allele frequency (MAF) in the population | Mutations with undetermined effect on protein function: mostly missense mutations | |
| IV | Rare benign and likely benign variants with an equitable allele representation (50% for heterozygotes and 100% for homozygotes) and high population frequency. Usually germline. They have no clinical significance for the treatment of malignant neoplasms. | Mutations with little or no clear effect on protein function: mostly missense mutations |
You can determine the mutation class in the report section with clinical guidelines.
- Links to the variant in embedded services:
is a module for visualization of variant on the genome,
is a variant details page in SNV Viewer ("Annotation" tab).
The variant interpretation text may be given below the variant row if it was added as described here.
Remove variants from the report#
A variant can be removed from the report by hovering over its row and clicking
on . Then you need to
confirm removing in the opened window:
This variant will no longer be included to the report (activated
button ) on SNV Viewer page, too.
Report Section with Clinical Guidelines#
- Corresponds to "Onco: Clinical Guidelines for onco relevant SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" template block.
- At the top of the section, there are the following fields:
- Oncological disease: Non-small cell lung carcinoma, Melanoma, Neoplasm of the pancreas, Breast carcinoma, Ovarian neoplasm, Prostate cancer, Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, Colorectal carcinoma;
- Stage (of the disease): I-IV;
- Stage details: Relapse, Progressing, Inoperable, Brain metastases;
- Therapy line (used to treat the patient's oncological disease at the time the sequencing sample material was collected): 1-4 line, Adjuvant or Neoadjuvant therapy, Perioperative, Preoperative or Induction chemotherapy);
- Mutation class (see description above).
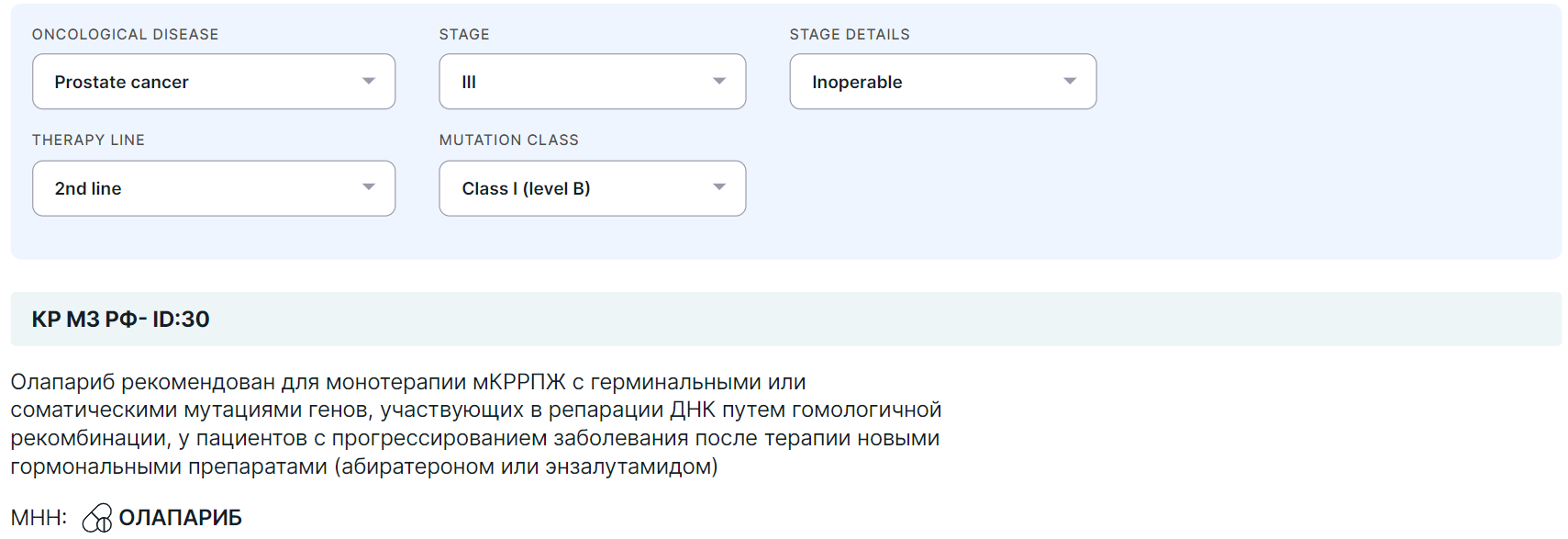
- If the fields required to unambiguously find clinical guidelines for the patient (oncological disease, stage, details) are not selected, then the recommendations will not be displayed.
Report export#
Onco-genetic testing report can be downloaded in PDF format.
To do this, click on the button in the
upper right corner of the report page.