ClinVar Phenotype Report
The report includes a condition (ClinVar phenotype) that has the risk of developing in the patient due to pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants discovered in patient sample and associated with this condition, and recommendations that can prevent this condition.
To obtain such a report, create a report template that includes "SNVs/Indels by ClinVar phenotypes" block.
The report is divided into three main sections: Report result and Recommendations, Detailed report and Excluded variants.
1. Report Result and Recommendations#
The sections includes:
- A condition (ClinVar phenotype) that has the risk of developing in the patient or patient's closest relatives due to pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants discovered in patient sample and associated with this condition. The report may flag conditions that are characteristic of a person of the opposite sex. This means that the variants found may not affect the risk of developing the condition in the patient but may be transmitted from patient to a person or may have been inherited by patient from a person who also may be at risk.
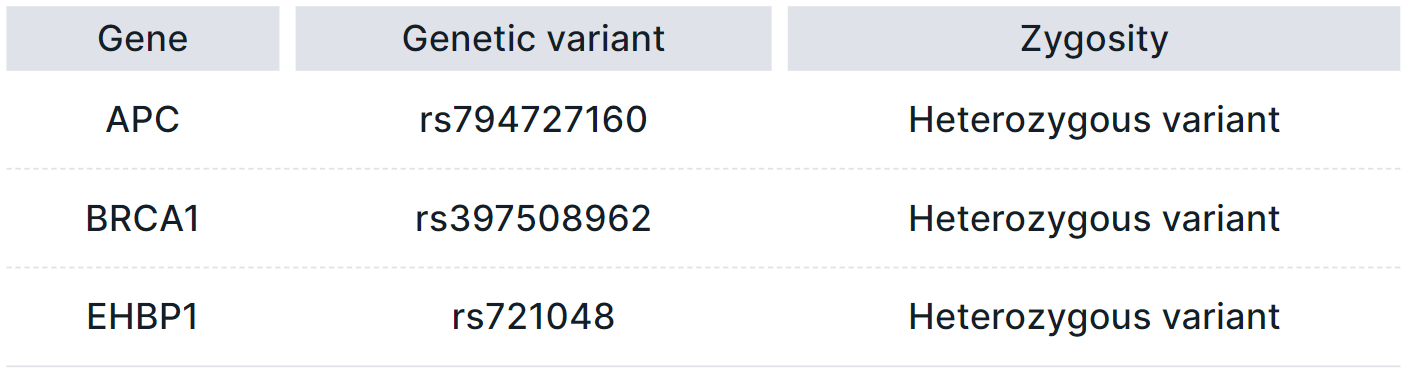
- Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants associated with the conditions listed above. Listed in a table with the following columns:
- Gene is the common name of the gene in which the variant is located;
- Genetic variant is a variant ID in dbSNP database (rsId);
- Zygosity type of the variant: heterozygous or homozygous.
- Recommendations for the patient (consultation with a medical geneticist).
- Information for the doctor: a brief summary of how the report is compiled.
2. Detailed Report#
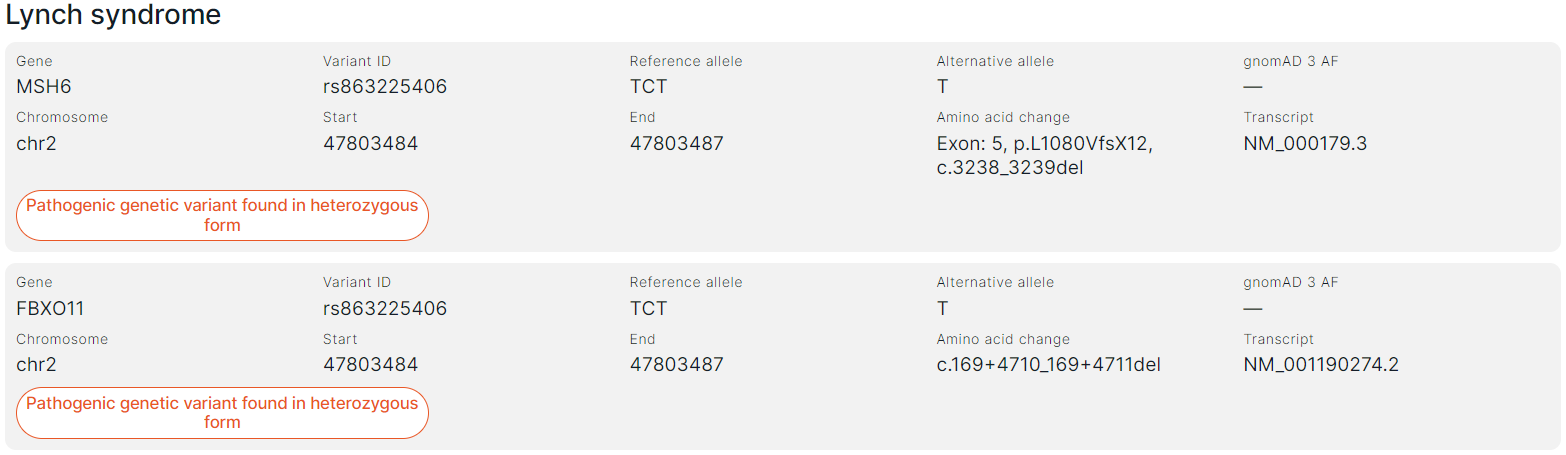
A detailed report of the conditions listed in the first section. For each state, the following is indicated:
- Name: corresponds to "Report name" field from the template.
- Variants discovered in the sample that are associated with the condition (with MedGen ID and/or ClinVar name in the template). Each variant meets the following conditions:
- Pathogenic or likely pathogenic in ClinVar ("Clinical significance" field);
- Not homozygous for reference (has at least one alternative allele);
- The total allele frequency in gnomAD 3 is above the frequency threshold for extremely rare pathogenic variants and below the frequency threshold for too frequent pathogenic variants (thresholds are set in the template).
- Recommendations that can help reduce the risk of this condition (added in the template).
3. Excluded Variants#
Contains variants that were excluded from the detailed report according to one of the following criteria (while these variants meet all of the above conditions for being included in the report):
- Criterion 1: variants with too high frequency in the human population (greater than 15%). Possible pathogenicity of these variants is inconsistent with such a high frequency.
- Criterion 2: variants that are homozygous and that have frequency of less than 1% in the human population. According to publication, these variants could be detected as a result of a genotyping error carried out using microarray technology.
- Criterion 3: variants that have a high probability of detection, expected based on the binomial
distribution and the probability of detecting a genetic variant among the identified populations.
The probability of the variant detection is below the reliability threshold, which is set
in the template.
The probability is calculated as (1 - Bin(n; m; p; 1)),
where Bin(n; m; p; 1) is the probability, expected based on the binomial distribution, that the variant is detected n times among m representatives (samples) of the population;
n is the number of representatives of the population (samples) in which this variant was detected;
m is the total number of representatives (samples) in the population;
p is the probability of detecting the variant in the human population (total allele frequency in gnomAD 3 database). If there is no data on the frequency in the population, then the probability is taken as 0.001.
Thus, variants are excluded from the report if they were detected more than n times among m samples of the population, but at the same time have a low frequency in the human population, i.e. possible pathogenicity of these variants is inconsistent with such a high frequency among representatives (samples) of the population.
The values of n and m are taken from the custom frequency database. If the database has not been uploaded into the system, variants will not be excluded by Criterion 3.
Each variant is presented in the report as follows:#
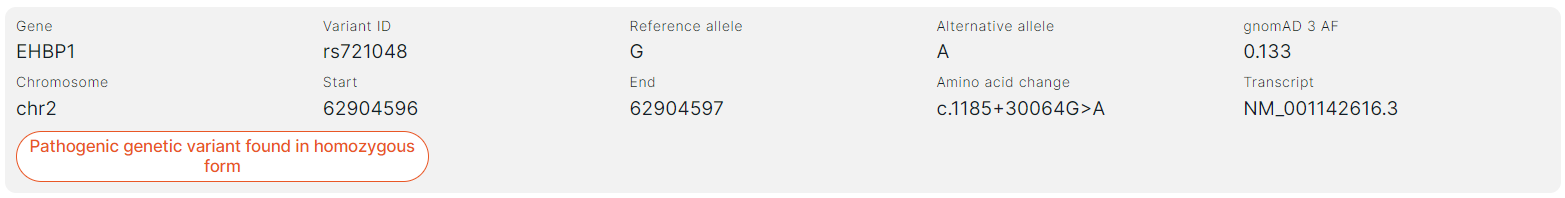
- Gene is the common name of the gene in which the variant is located.
- Variant ID is a variant ID in dbSNP database (rsId).
- Reference allele of the variant.
- Alternative allele of the variant.
- gnomAD 3 AF is the total allele frequency in gnomAD v3 database.
- Chromosome is the chromosome in which the variant is located.
- Start is the start position of the variant on the chromosome.
- End is the end position of the variant on the chromosome.
- Amino acid change: exon number in the transcript that the variant affected; amino acid and nucleotide substitutions using the HGVS notation. Amino acid substitution: “p.” prefix (protein) + reference amino acid + amino acid position in protein + new amino acid resulting from the substitution. Nucleotide substitution: “c.” (coding; for a substitution in the coding sequence) or “n.” (non-coding; for a substitution in the non-coding sequence) + genomic position of the substituted nucleotide + reference allele > alternative allele.
- Transcript is the main transcript ID from RefSeq database (NM_xxxxxx.x).
- An indication of the variant zygosity: heterozygous or homozygous.
- For variants excluded from the detailed report, there is an indication of the criterion by which they were excluded.
Reports export#
ClinVar phenotype report can be downloaded in PDF format.
To do this, click on the button in the
upper right corner of the report page.