Variant Details Page
The variant details page may include tabs with the following information:
- Detailed variant annotation;
- Sample and Patient info;
- Information about occurrences of the variant in other samples;
- ACMG classification;
- Scientific publications associated with the variant;
- Clinical guidelines (if the variant is onco relevant);
- Variant report.
To go to the variant details page from SNV Viewer,
click on in the variant row.
On the variant details page, the main information about the variant is given at the top:
- The name of the gene in which the variant is located;
- Nucleotide substitution: either in the HGVS notation (HGVSc = prefix (“c.” (coding; for a substitution in the coding sequence) or “n.” (non-coding; for a substitution in the non-coding sequence)) + genomic position of the substituted nucleotide + reference allele > alternative allele), or as a substitution like "g." prefix (genomic; for a linear genomic reference sequence) + the variant start position in the genome + reference allele > alternative allele);
- The variant position in the genome (chromosome + start position);
- Nucleotide substitution (reference allele > alternative allele);
- The transcript ID chosen as main for the variant from Ensembl database (ENSTxxxxxxxxxxx);
- The exon number in the transcript which is affected by the variant;
- The variant consequence for genes; see possible consequences here;
- Link to the variant in dbSNP database.
To include a variant to the report from the details page,
turn on  . You will
see "Reporting" tab.
Variants included to report will be included in report blocks
of "SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" type.
To remove a variant from the report, turn the switch back off. Variants included to report can also
be removed from report on the page of the report itself.
. You will
see "Reporting" tab.
Variants included to report will be included in report blocks
of "SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" type.
To remove a variant from the report, turn the switch back off. Variants included to report can also
be removed from report on the page of the report itself.
If a pathogenicity class has been determined for a variant,
it is automatically included to the sample interpretation results.
If you want to exclude a variant from the interpretation results from the variant details page, turn off the
corresponding toggle  .
.
To pin a variant in SNV Viewer table (read more about pinned
variants here) from the details page,
click on . To unpin, click again on the same button
.
To open the built-in module for visualization of variant on the genome (Integrative Genomics Viewer; IGV),
click on ![]() .
.
To close the variant details page, click on .
The pathogenicity scale in the upper right corner of the page is described in the corresponding section:

Adding Variant Interpretation#
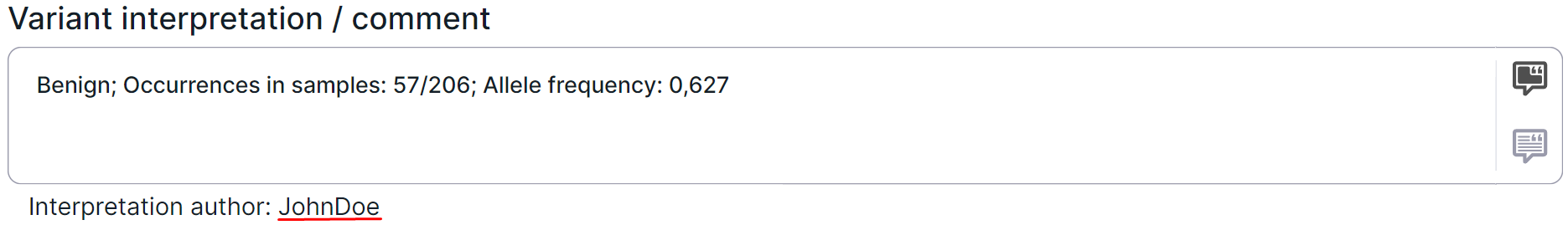
A variant interpretation is a comment with important information about the variant added by the user. Where to find it after adding is described here. To add or edit a variant interpretation, do the following:
- Click on the input box:

- Enter text or quote any text from the variant details page in one of the following ways:
- Click on
and then click on the desired text. The text will appear in the interpretation input box. This way is useful if you want to cite the entire text of the element (e.g. full gene name).
- Highlight the desired text and then
click on
. The selected text will appear in the interpretation input box. This way is useful if you want to cite only a part of the element's text (e.g. one sentence from the article abstract).
After adding an interpretation, the interpretation author (the name of the user who interpreted the variant) will be displayed under the input box:
"Annotation" tab#
The "Annotation" tab includes those annotation sections that contain at least one non-empty annotation field. Annotation sections correspond to the variant details panel tabs, you can find a detailed description of the tabs here.
"Sample" tab#
The "Sample" tab may contain two sections:
- Sample Info corresponds to the sample info
from "Main" tab of the sample page. Most of the fields (except for
Sequencing Type and Capture Kit) can be edited both on the sample page and here, on "Sample" tab.
The section contains the following sample information:
- SEQUENCING TYPE: Panel (targeted sequencing), WES (whole-exome sequencing), WGS (whole-genome sequencing), Low-pass WGS (whole-genome sequencing with low coverage), UNKNOWN (the sequencing type may not be detected for some samples in VCF format). Detected automatically by Genomenal, may be based on Sequencing Type and Capture Kit selected while adding sample set. The type can be changed on "Parameters" tab ("Sequencing Type" parameter: "WGS" option corresponds to "WGS" or "Low-pass WGS" type, "Targeted selection" option corresponds to "Panel" or "WES" type).
- SAMPLE COLLECTION DATE is the date in the format M/d/yyyy. Can be specified by clicking on the value field.
- CAPTURE KIT is a panel used in targeted selection. Detected automatically by Genomenal, or by user while adding sample set. If the capture kit is defined incorrectly, it can be changed on Parameters tab. You can use both built-in capture kits (standard panels often used in sequencing) and custom capture kits uploaded by the user (on "Capture kits" page).
- SAMPLE LOCATION (ORGAN) is the organism part from which the sample was taken for sequencing. Can be specified by clicking on the value field.
- METHODOLOGY is the method of extracting the sample. Can be specified by clicking on the value field.
- ONCOLOGICAL DISEASE, STAGE and STAGE DETAILS are the patient's oncological disease, its stage and stage details, which were defined for the patient at the time the sample was taken for sequencing.
- THERAPY LINE is the therapy line that was being used to treat the patient's disease at the time the sample was taken for sequencing.
- INTERPRETATION RESULTS are the sample interpretation results, i.e. information on the number of mutations with a
particular pathogenicity class discovered in the sample
and included to the interpretation results.
Read more about completing/resuming sample
interpretation below.
It may include information about SNVs/Indels, designated "SNV", and information about copy number variations,
designated "CNV". The information is presented as follows:
- pathogenicity icons indicating the number of mutations with this pathogenicity:
- pathogenic mutations:
;
- likely pathogenic mutations:
;
- mutations of uncertain significance:
;
- likely benign mutations:
;
- benign mutations:
.
- pathogenic mutations:
- message "Interpretation not completed" if mutations with a particular pathogenicity class were included to the interpretation results, but the sample interpretation was not completed.
- message "No pathogenic variants found" if the sample interpretation has been completed, but no mutations with a particular pathogenicity class have been included to the interpretation results.
- empty value if sample interpretation was not completed and no mutations with a particular pathogenicity class were included to the interpretation results.
- pathogenicity icons indicating the number of mutations with this pathogenicity:
- Patient Info corresponds to the patient info from the patient page.
This section is presented on the page if the sample in which the variant was discovered belongs to a
patient (and not just a run). The field can be edited both on the patient page and here, on the "Sample"
tab.
The section contains the following patient information:
- PATIENT ID is a code entered when creating a patient (you can edit it by clicking on the code). Can include any characters.
- LAST NAME and FIRST NAME of the patient. Can be specified by clicking on the value fields.
- DATE OF BIRTH of the patient in M/d/yyyy format. Can be specified by clicking on the value field.
- SEX of the patient: male, female. Sex can be specified by clicking on the value field and selecting the value from the drop-down list.
- PROVIDED DIAGNOSIS is the patient's diagnosis at the time the sample was taken for sequencing. Can be specified by clicking on the value field.
Sample Interpretation#
One way to complete the sample interpretation is described here. Other ways are described here. The sample interpretation is interpretation of the pathogenicity of mutations discovered in the sample. To add the variant to the sample interpretation results, you need to:
- determine the variant pathogenicity class (see here);
- include the variant to interpretation results. This occurs automatically when the pathogenicity class of the variant is determined. In addition, potential findings can be included to interpretation results, as described here.
note
If necessary, variants can be added to the sample interpretation results after the interpretation is complete.
To complete interpretation,
click on  on the "Sample" tab of
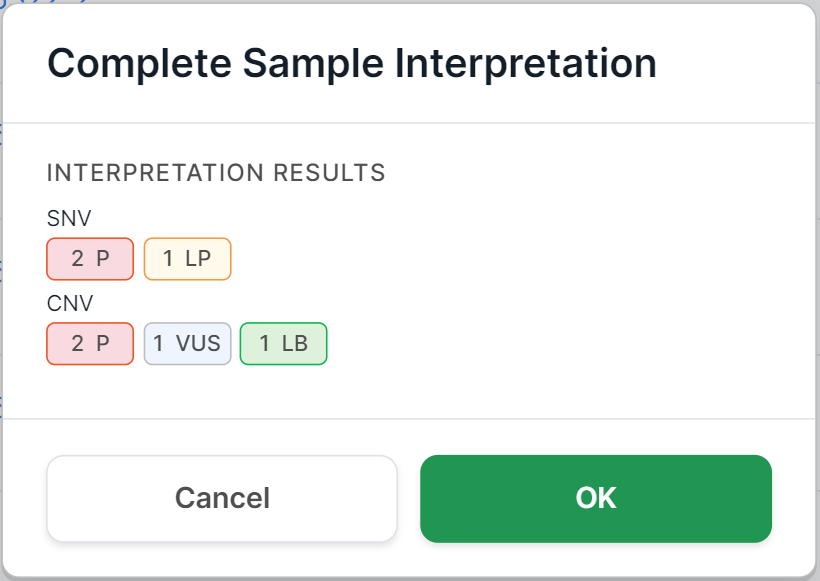
the variant details page. You will see a confirmation window. For non-tumor samples, it looks like this:
on the "Sample" tab of
the variant details page. You will see a confirmation window. For non-tumor samples, it looks like this:
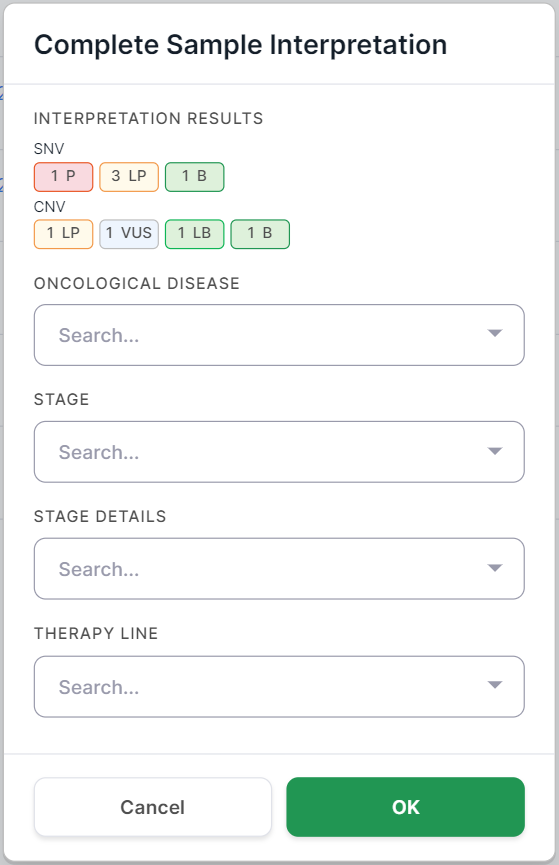
And for tumor samples, it also includes fields about the oncological disease:
The "Interpretation results" field provides information about the number of mutations with a certain pathogenicity class discovered in the sample and included to the interpretation results. The field may include information about SNVs/Indels, designated "SNV", and information about copy number variations, designated "CNV". The information is presented in the form of pathogenicity icons indicating the number of mutations with this pathogenicity:
- pathogenic mutations:
;
- likely pathogenic mutations:
;
- mutations of uncertain significance:
;
- likely benign mutations:
;
- benign mutations:
.
If no mutations with a particular pathogenicity class have been included to the interpretation results, then the field value will be "No pathogenic variants found".
For variants discovered in tumor samples, you can also specify the oncological disease, its stage, and stage details which were defined for the patient, as well as the therapy line used to treat the patient's disease, at the time the sample was taken for sequencing.
To confirm completing interpretation, click on .
To resume completed interpretation,
click on  .
.
"Occurrences" tab#
Among other samples uploaded by the user to the system, or group analyzes created by the user, information on the occurrences of the following variants can be found:
- the same variants as the variant whose details page is open. The variants found completely coincide with this variant in terms of origin (somatic or germline), chromosome, start position, reference and alternative allele and gene. The sites of the found variants contain at least one alternative allele (i.e., they have the genotype 1/1, 1|1, 0/1, 1/0, 0|1, 1|0, 1/., 1|., ./ 1, .|1, 1, 0/0/1, 0/2, 1/2, etc.)
- all variants in the same position as the variant whose details page is open. The variants found contain at least one alternative allele and match this variant in terms of origin, chromosome, and start position.
- variants in position ± 10 bp or ± 20 bp from the starting position of the variant whose details page is open. The variants found coincide with this variant in terms of origin. Their starting positions are located within the range of ± 10 b.p. or ± 20 b.p. from the starting position of this variant. The sites of the found variants contain at least one alternative allele.
To the right of the buttons for switching the search for the variants described above, there is information about the number of such variants found in other samples:
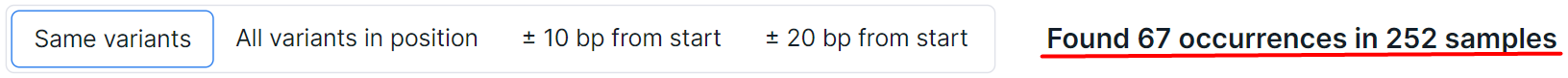
The samples count includes all samples ever uploaded to the system (including deleted ones) for which the variants discovery stage (for samples uploaded in FASTQ or BAM format) or the variants annotation stage (for samples uploaded in VCF, TXT or TSV format) was successfully completed. Thus, to calculate the occurrences of the somatic variant, those samples uploaded in FASTQ or BAM format, in which the "Somatic SNVs/Indels discovery" stage has been successfully completed, and those samples uploaded in VCF, TXT or TSV format, in which the "Somatic SNVs/Indels annotation" stage has been successfully completed, are taken into account. To calculate the occurrences of the germline variant, samples in FASTQ or BAM format with successfully completed stage "Germline SNVs/Indels discovery" and samples in VCF, TXT or TSV format with successfully completed stage "Germline SNVs/Indels annotation" are taken into account.
Below are cards with the variants found. Card example:
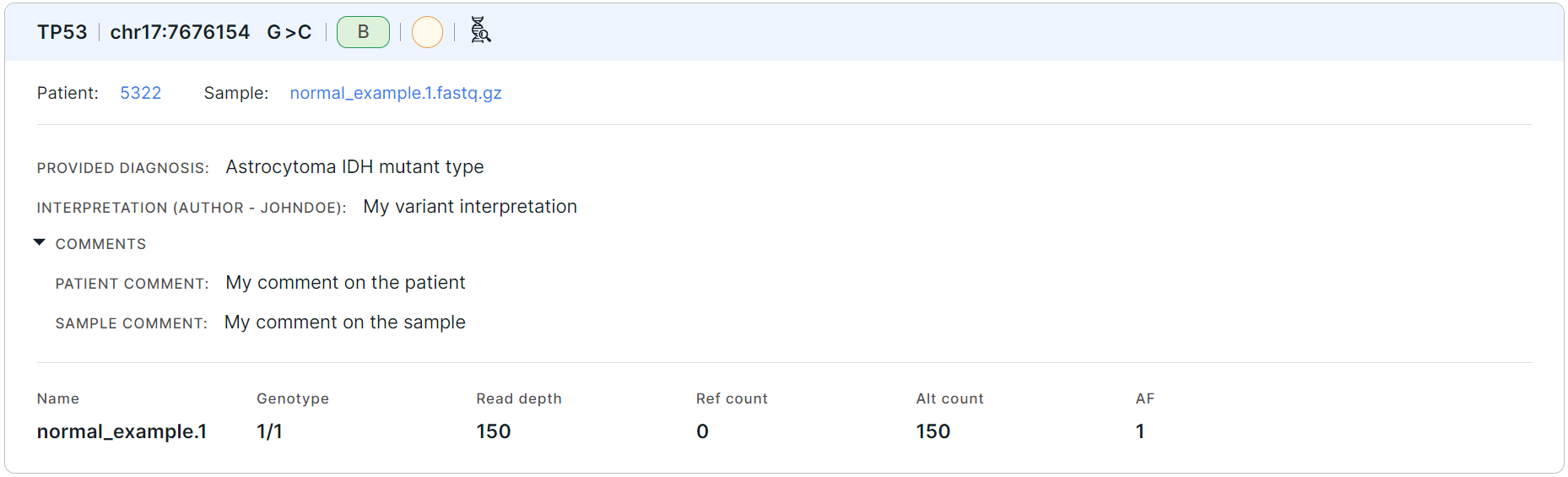
The variant card includes:
- the name of the gene in which the variant is located;
- the variant position: chromosome + start position;
- the variant alteration: reference allele > alternative allele;
- the variant pathogenicity (if
it has been defined for this variant;
if the pathogenicity class requires confirmation,
then next to the pathogenicity icon there will
be
);
- the variant significance (if it has been defined by the user);
- link to the found variant details page:
(if the sample in which the variant was discovered is deleted, then there will be no link to the variant);
- links to the patient and/or run, in which the sample with the variant is uploaded (if the patient and/or run is deleted, then the patient code or the run name will be indicated with a deletion mark instead of the links);
- link to the sample in which the variant was discovered (if the sample was deleted, then the sample's file name will be indicated with a deletion mark instead of the link);
- the patient's diagnosis made at the time the sequencing sample material was taken (can be defined on the patient page or on "Sample" tab of the variant details page);
- the variant interpretation (a variant can be interpreted on the variant details page or panel; in brackets, there is the name of the user who interpreted the variant);
- section with comments, which is displayed only if at least one of the comments is present: patient comment, run description, or sample comment;
- information on sequencing samples::
- Name is a name of the sample, for which the analysis was performed.
- Genotype is an allele combination for this sample (0 - reference allele, 1 - first alternative allele, 2 - second alternative allele etc.), divided by ”/” (for unphased genotype) or “|” (for phased genotype). The number of alleles suggests ploidy of the sample.
- Read depth is a total number of reads of the sequence overlapping the variant position for this sample.
- Ref count is a reference allele reads count for this sample.
- Alt count is an alternative allele reads count for this sample.
- AF is an allelic frequency for this sample.
At the end of the page, there is information about the variant occurrences in group analyzes created by the user:

There are also variant cards with the following information:
- the name of the gene in which the variant is located;
- the variant position: chromosome + start position;
- the variant alteration: reference allele > alternative allele;
- the variant pathogenicity (if
it has been defined for this variant;
if the pathogenicity class requires confirmation,
then next to the pathogenicity icon there will
be
);
- the variant significance (if it has been defined by the user);
- link to the found variant details page:
(if the group analysis is deleted, then there will be no link to the variant);
- link to the group analysis in which the variant was discovered (if the group analysis was deleted, then the group analysis name will be indicated with a deletion mark instead of the link);
- the variant interpretation (a variant can be interpreted on the variant details page or panel; in brackets, there is the name of the user who interpreted the variant);
- group analysis comment (if it was added on the analysis page).
"ACMG Classification" tab#
The tab includes the variant interpretation criteria developed by ACMG. The tab is described in detail in the corresponding section of the documentation.
"Literature" tab#
The tab includes scientific publications associated with the variant found in NCBI LitVar. Searching for variants in the database can take some time, so when you first open "Literature" tab for a variant, you may see the message "Looking for literature in LitVar. It can take about a minute." In this case, just wait until the literature is loaded. If literature for a variant was not found in LitVar, you will see the message "Literature not found in LitVar. You can: Add PMID or Search on Google Scholar." (see below how to add a publication by PMID and to search publications on Google Scholar).
An example of a publication card found for variant TP53:c.215C>G:
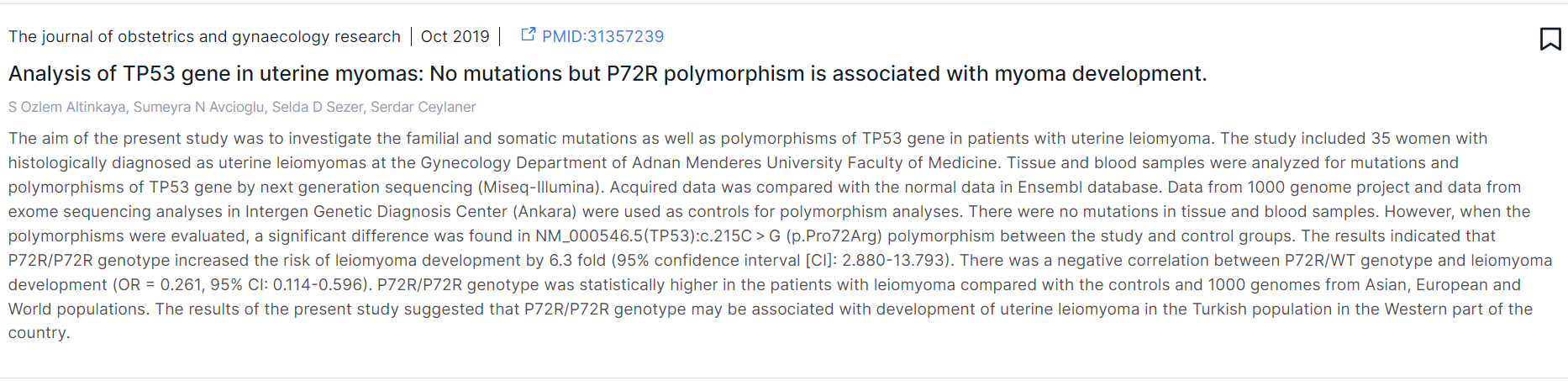
For each article, there are journal name, publication date, link to the article
in PubMed (PMID), title, authors, and abstract of the article.
You can add an article to curated (bookmarked) articles by
clicking on . Then, you can filter articles and see only curated ones by clicking on
. To remove an article from curated, click on
.
To search for a specific publication among the found ones, use the search box.
You can add the missing publication to the list. To do this:
- Click on
;
- In the opened window, enter the publication's PMID and
click on
:

You can use Google Scholar to search for additional publications associated
with the variant. To do this, click on  .
.
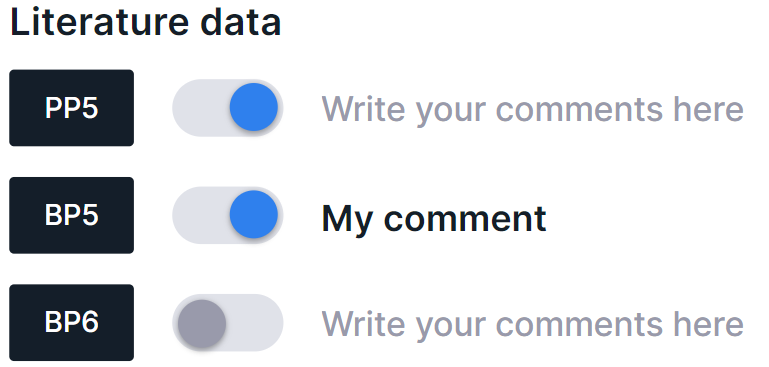
Link a publication with an ACMG criterion#
A publication can be associated with an ACMG criterion/criteria. You can find a description of the ACMG criteria here. To link a publication with criterion, click on the publication card, and then on the criterion toggle. You can also leave a comment here:
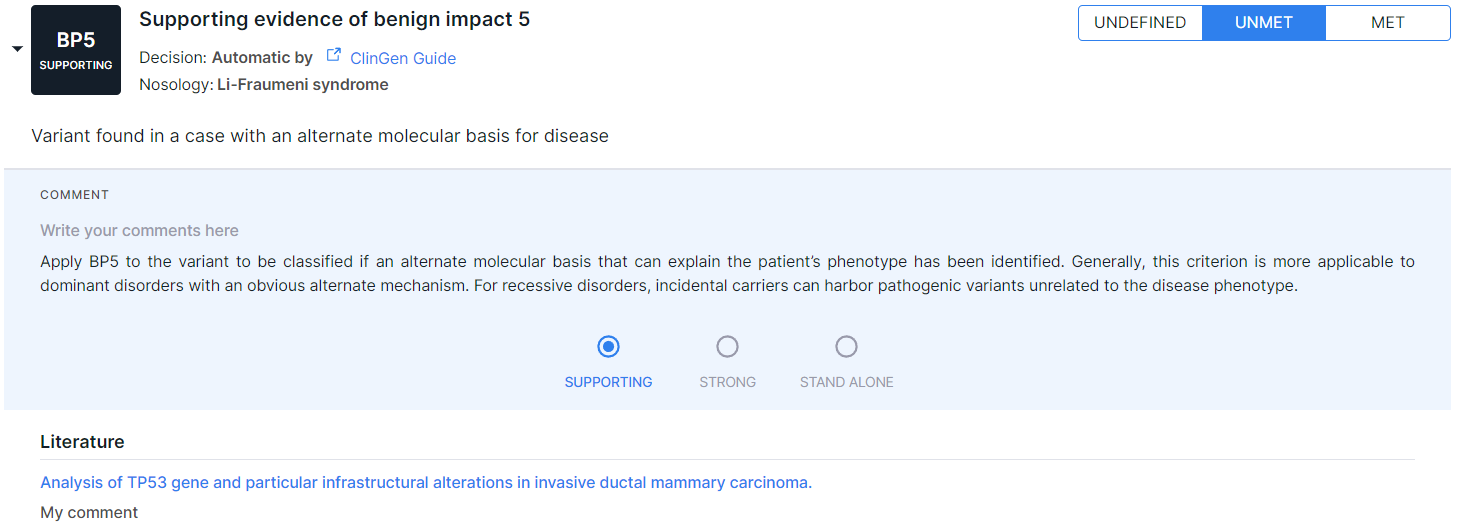
Once a publication is linked with an ACMG criterion, it is automatically added to curated (bookmarked) publications. If you remove all connections of a publication with criteria (turn off all toggles), then it will be automatically removed from the curated publications. The publication linked to the criterion (active link to the article in PubMed) and the comment will be located in "Literature" section (in the expanded area of criterion on "ACMG Classification" tab):
"Clinical Guidelines" tab#
The "Clinical Guidelines" tab appears on the variant details page only if this variant is onco relevant for non-small cell lung carcinoma, melanoma, neoplasm of the pancreas, breast carcinoma, ovarian neoplasm, prostate cancer, anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, or colorectal carcinoma. The tab contains clinical guidelines developed by RUSSCO, АОР, Clinical Recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (КР МЗ РФ), NCCN, ESMO for patients with certain oncological disease (with which the variant is associated), its stage, stage's details and therapy line. The tab is described in detail in the corresponding section of the documentation.
"Reporting" tab#
On the "Reporting" tab, you can include a variant to the report, see how the variant information will look in the report, and export the report with this variant.
To include a variant to the report from the variant details page, turn on the corresponding
toggle  . Variants included to report will
be included in report blocks
of "SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" type.
To remove a variant from the report, turn the switch back off. Variants included to report can also be
removed from report on the page of the report itself.
. Variants included to report will
be included in report blocks
of "SNVs/Indels selected by user for reports" type.
To remove a variant from the report, turn the switch back off. Variants included to report can also be
removed from report on the page of the report itself.
After including a variant to the report, you will see a preview of the variant in the report:
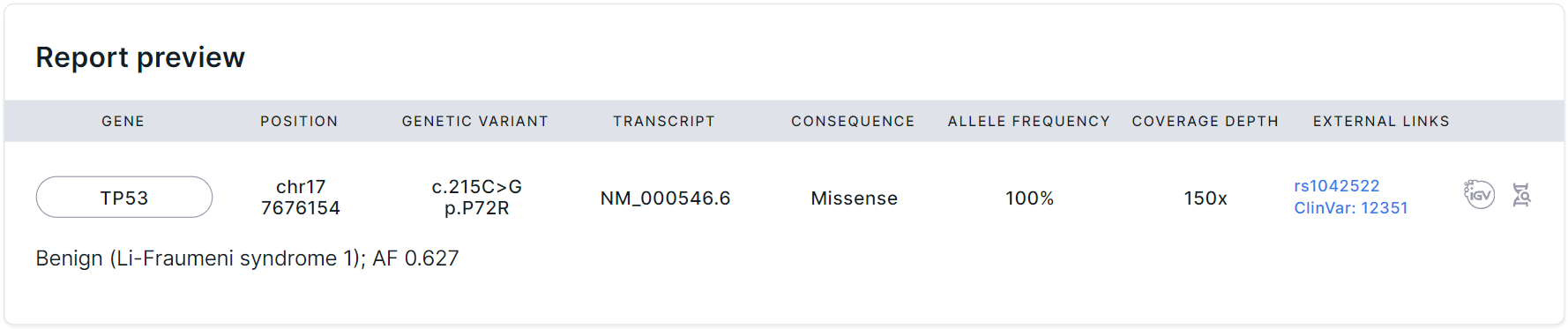
In the report, the variant is displayed in a table with the following columns:
- Gene is the common name of the gene in which the variant is located. If you click on a gene, you will see a window with all the gene transcripts:

You can find the description of the transcripts' table columns here.
- Position is a coordinate of the variant in the genome (chromosome + start position).
- Genetic variant is the nucleotide and amino acid substitutions using the HGVS notation. Nucleotide substitution: “c.” (coding; for a substitution in the coding sequence) or “n.” (non-coding; for a substitution in the non-coding sequence) prefix + genomic position of the substituted nucleotide + reference allele > alternative allele. Amino acid substitution: “p.” prefix (protein) + reference amino acid + amino acid position in protein + new amino acid resulting from the substitution.
- Transcript is the main transcript ID from the RefSeq database (NM_xxxxxx.x). If you click on a transcript, you will see the same window with all the gene transcripts, as when you click on the "Gene" field.
- Consequence is the effect of the variant on genes. A detailed description of the possible values can be found here.
- Allele frequency is an alternative allele frequency for the sample (in percentages).
- Coverage depth is a sequencing depth; the total number of reads of the sequence overlapping the variant position for the sample.
- External links are links to pages with variant information in dbSNP, ClinVar and COSMIC (if it was uploaded as a custom annotation).
- Links to the variant in embedded services:
is a module for visualization of variant on the genome,
is a variant details page in SNV Viewer ("Annotation" tab).
Under the variant row in the table, there may be the variant interpretation added as described above.
To export a variant report in PDF format,
click on .