Somatic SNVs/Indels discovery and annotation
Somatic SNVs/Indels discovery#
After the "Variant discovery preprocessing" stage has been successfully completed, somatic SNVs/Indels discovery can be initiated for tumor samples if the stage is included in the analysis workflow.
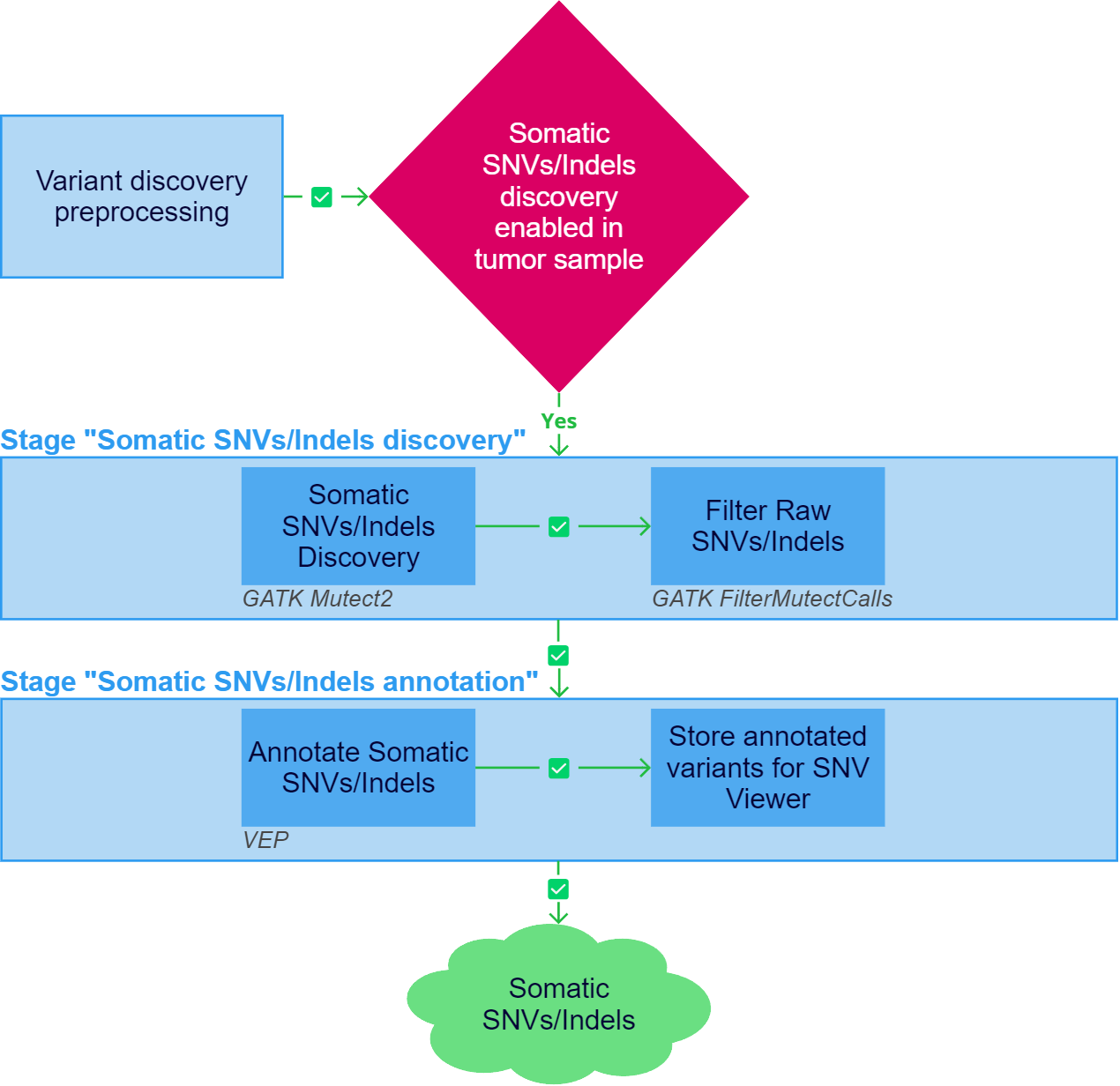
1. Somatic SNVs/Indels Discovery#
Somatic single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and short insertions/deletions (indels) calling is performed using GATK Mutect2.
I. Dividing data into intervals#
To speed up the process and save resources, the Scatter-Gather task divides the input data into 64 genomic intervals. If the sample capture kit is defined, the data is divided using bedtools intersect, which screens for overlaps between distinct genomic intervals and capture kit intervals.
II. Variant calling#
Variant calling in each of the resulting intervals is performed using GATK Mutect2. Mutect2 works primarily by matching variants in tumor and control samples (tumor-normal mode). In this case, it includes logic to skip emitting variants that are clearly present in the germline based on provided evidence in the matched normal. This is done at an early stage to avoid spending computational resources on germline events. If the variant's germline status is borderline, then Mutect2 will emit the variant to the callset for subsequent filtering by FilterMutectCalls and review. Mutect2 is also suitable for calling variants in a tumor sample without a control sample (tumor-only mode), but this calling has a high number of false positives.
It is recommended to use a panel of normals (PON), i.e. a panel made from from normal samples (i.e. samples derived from healthy tissue that is believed to not have any somatic alterations), to capture recurrent technical artifacts in order to improve the results of the variant calling analysis. Normals that are as technically similar as possible to the tumor (same exome or genome preparation methods, sequencing technology and so on) should be used to include in a PON. As a result, the most important selection criteria for choosing normals to include in a PON are the technical properties of how the data was generated. The more accurate the panel, the more specific the analysis becomes and more variants can be discovered. By default, the analysis is performed with "Basic panel of normals". To select a different PON or to perform the analysis without any panel, select the corresponding option in the parameters.
The gnomAD database is used as a resource containing population allele frequencies of common and rare variants.
By default, soft clipped bases (i.e. bases from the ends of reads that do not align with the reference sequence) are analyzed when calling variants. This is controlled by the corresponding setting.
To eliminate possible substitution errors that occur in one strand before sequencing, an orientation bias filter is applied. The filter consists of three stages. Mutect2 includes the first stage of filtering, such as collecting F1R2 counts (F1R2 is a read pair if the sequence of bases in Read 1 maps to the forward strand of the reference, and the sequence of Read 2 to the reverse strand of the reference).
III. Combining the discovered variants#
GATK MergeVcfs combines files with variants discovered in distinct genomic intervals into a single variant file in VCF format. The resulting file with all somatic variants discovered in a sample is compressed into a GZIP archive using bgzip. It can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Somatic SNVs/Indels Discovery" task details ("Download VCF_GZ"). You can also open this file in the IGV browser by clicking on the "Open in IGV Browser" link. In addition, the VCF file is indexed using tabix. The resulting index file can be downloaded in the same section ("Download VCF_TBI").
IV. Merging stats#
GATK MergeMutectStats merges the stats files obtained from previously split intervals. The resulting file in TSV format can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Somatic SNVs/Indels Discovery" task details ("Download Mutect2 stats TSV"). You can also open it in Google Sheets.
V. Learning the read orientation model#
The second step of orientation bias filter is the work of GATK LearnReadOrientationModel. It gets the maximum likelihood estimates of artifact prior probabilities in the orientation bias mixture model filter. As a result, artifact prior tables are generated for each tumor sample. The resulting file in tar.gz format containing artifact prior tables can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Somatic SNVs/Indels Discovery" task details ("Download Read orientation model TAR_GZ").
2. Filter Raw SNVs/Indels#
I. Tabulating Pileup metrics#
GATK GetPileupSummaries tabulates Pileup metrics for inferring contamination. To do this, it summarizes counts of reads that support reference, alternate and other alleles for given sites. The resulting table in TXT format can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Filter Raw SNVs/Indels" task details ("Download Pileup table TXT").
II. Generating contamination table#
Based on the data obtained by GetPileupSummaries in the previous step, GATK CalculateContamination calculates the fraction of reads coming from cross-sample contamination. The resulting table provides the fraction contamination of each analyzed sample. The table can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Filter Raw SNVs/Indels" task details ("Contamination table TXT").
III. Filtering variants#
GATK FilterMutectCalls filters somatic SNVs and indels called by Mutect2. To do this, it uses:
- the contamination table created in the previous step;
- the Mutect stats file obtained in the stats merging step;
- a file containing artifact prior tables obtained in the learn read orientation model step.
The resulting file is compressed into a GZIP archive using bgzip. It can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Filter Raw SNVs/Indels" task details ("Download VCF_GZ"). You can also open this file in the IGV browser by clicking on the "Open in IGV Browser" link. In addition, the VCF file is indexed using tabix. The resulting index file can be downloaded in the same section ("Download VCF_TBI").
Somatic SNVs/Indels annotation#
After the "Somatic SNVs/Indels discovery" stage has been successfully completed, somatic SNVs/Indels annotation is performed.
1. Annotate Somatic SNVs/Indels#
Annotation of SNVs/Indels in the file with data from the RefSeq, 1000 Genomes, dbNSFP, dbSNP, gnomAD 3, gnomAD 4, ClinVar, CADD, SpliceAI, ENIGMA databases.
Determination of the effect of SNVs/Indels on genes, transcripts, and protein sequence, as well as regulatory regions, using Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor (VEP):
PolyPhen predicts possible impact of an amino acid substitution on the structure and function of a protein using straightforward physical and comparative considerations.
A flag indicating if the transcript is the canonical transcript for the gene is added.
Allele number from VCF input is identified.
Affected exon and intron numbering is added.
HGVS nomenclature based on Ensembl stable identifiers is added.
Upstream variant consequences are determined if the upstream (5') distance between a variant and a transcript is more than 2000 bp. Downstream variant consequences are determined if the downstream (3') distance between a variant and a transcript is more than 1000 bp.
The resulting file with raw annotated SNVs/Indels in TSV format can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Annotate Somatic SNVs/Indels" task details ("Download Raw annotated TSV"). You can also open it in Google Sheets.
The resulting file with annotated SNVs/Indels without duplicates in TSV format can be downloaded in the same section ("Download All variants TSV"). You can also open it in Google Sheets. The same file in CSV format can be downloaded from the same place ("Download All variants CSV").
Converting TSV results to VCF.
GATK FixVCFHeader replaces or fixes a VCF header.
The file is compressed into a GZIP archive using bgzip. The resulting file can be downloaded in the "Result files" section in the "Annotate Somatic SNVs/Indels" task details ("Download All variants VCF_GZ"). You can also open this file in the IGV browser by clicking on the "Open in IGV Browser" link.
The file is indexed using tabix. The resulting index file can be downloaded in the same section ("Download All variants VCF_TBI").
Calculating variants' statistic.
2. Store annotated variants for SNV Viewer#
- Saving results for display in SNV Viewer, i.e. an embedded service for viewing and analyzing variants.
- Adding information about the variant occurrence in other samples of the user.
After the "Somatic SNVs/Indels annotation" stage, the analysis can proceed with report generation.
info
If you want to add a track with somatic SNVs/Indels discovered by the analysis of the sample you uploaded to Genomenal to your desktop IGV, you can do so via a link. Open the details of the necessary task ("Somatic SNVs/Indels Discovery", "Filter Raw SNVs/Indels", "Annotate Somatic SNVs/Indels") and do the following:
- Right-click the variant file link (depending on the selected task, this may be the link "Download VCF_GZ", "Download All variants VCF_GZ" or "Download Filtered variants VCF_GZ") and select the "Copy link address" option.
- Upload the track via URL to your desktop IGV, as described here.
- Right-click on the download link for the index file corresponding to the annotation file ("Download VCF_TBI", "Download All variants VCF_TBI" or "Download Filtered variants VCF_TBI") and select the "Copy link address" option.
- Add the index via URL to the corresponding field in IGV.
- Click "OK". Done! The track with somatic SNVs/Indels discovered in the sample is added to IGV.